- Review
Bioactive Compounds for Topical and Minimally Invasive Cellulite Treatment and Skin Rejuvenation
- Aura Rusu,
- Raluca-Daniela Mazilu and
- Gabriel Hancu
- + 4 authors
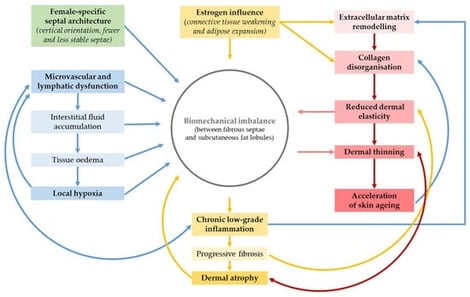
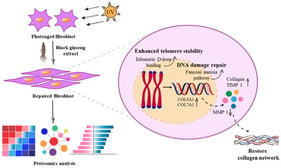
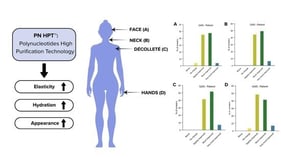
Cellulite, a multifactorial condition affecting approximately 98% of women, is characterised by dermal and subcutaneous architectural changes that compromise skin texture and elasticity. Its progression is closely linked to hormonal, vascular, and inflammatory factors, as well as ageing-related extracellular matrix degradation. This review critically evaluates bioactive compounds incorporated into topical and minimally invasive formulations for the management of cellulite and skin rejuvenation. A comprehensive literature search was conducted across major scientific databases and cosmetic ingredient repositories, focusing on active ingredients with demonstrated efficacy in enhancing skin structure. Key compounds include capsaicin, forskolin, L-carnitine, caffeine, retinol, and extracts from plants such as Centella asiatica, which act via lipolysis, improved circulation, and antioxidant effects. Minimally invasive agents, such as deoxycholic acid and poly-L-lactic acid, complement these strategies by inducing adipocytolysis and neocollagenesis, thereby improving skin firmness and contour. Evidence indicates that multi-active formulations combining lipolytic agents with antioxidants and collagen-stimulating molecules yield synergistic benefits, reducing adipose protrusion and improving skin firmness. However, heterogeneity in study design and the lack of standardised evaluation methods limit firm conclusions. Further studies should validate efficacy and optimise delivery. Integrated topical and injectable therapies represent a promising, multifunctional approach to addressing cellulite and age-related skin changes.
6 February 2026